The new update to Windows 10, dubbed 1903, is to include a unique new feature—the release will segregate 7GB of hard disk space, reserving it exclusively for Windows updates.
This feature will eliminate the need to manually make space for large updates, ensuring that the process of updating is smooth and user-friendly.
However, the feature may not be popular with those who have limited storage space or with to control storage allocation themselves.
No More Error Messages
The update has been developed in response to a bug that delivered an error message when previous updates failed to install due to inadequate space.
Windows did not previously have the ability to check for adequate space before initiating updates.
This resulted in users being presented with an error message that then required them to create disk space by either manually deleting files or moving files to external storage in order to enable the update to continue.
The reserved 7GB will ensure that there is adequate space for future updates including temporary setup files.
Reserved Storage for Temporary Files
Apart from the Windows updates, there are other files on your computer that can occupy the reserved storage. These can include cache data, optional OS features and temporary files.
Temporary OS files will automatically be stored in the reserved space where they will be deleted when the space is needed for a new update.
Microsoft’s Windows 10 Storage Sense feature will also help to manage temporary files that get dumped in the allocated 7GB and remove them as they become irrelevant.
However, if the reserved space does become full, for whatever reason, Windows updates will use space outside of the allocated 7GB.
7GB Is a Starting Point
Microsoft believes that allocating 7GB of disk space specifically for the update process should enable future updates to be installed smoothly without the need for any manual deletion.
However, according to Microsoft, this 7GB is just a starting point and it seems likely that it could increase in the future.
Whatever the size, this could create problems for users who have PCs with limited storage space, such as some of the cheaper 32GB models on the market.
Unfortunately, increasing update sizes makes it all the more important for new PC purchases to have adequate disk space.
Options Available to Users
While there will be some options for controlling the amount of reserved space that is allocated, it appears that Microsoft’s wording is misleading.
In its release announcement, Microsoft explains how you can reduce the amount of space required for reserved storage on your device by uninstalling optional features (or languages) that you are not using.
However, this is after stating that the amount of storage space set aside by Windows increases to allow for these optional features.
Consequently, it seems that removing optional features and languages only reduces the reserved space back to the original 7GB.
Either way, this is still an option that some may choose to utilize in order to prevent the reserve space going significantly over the 7GB.
Follow These Steps to Remove Optional Features:
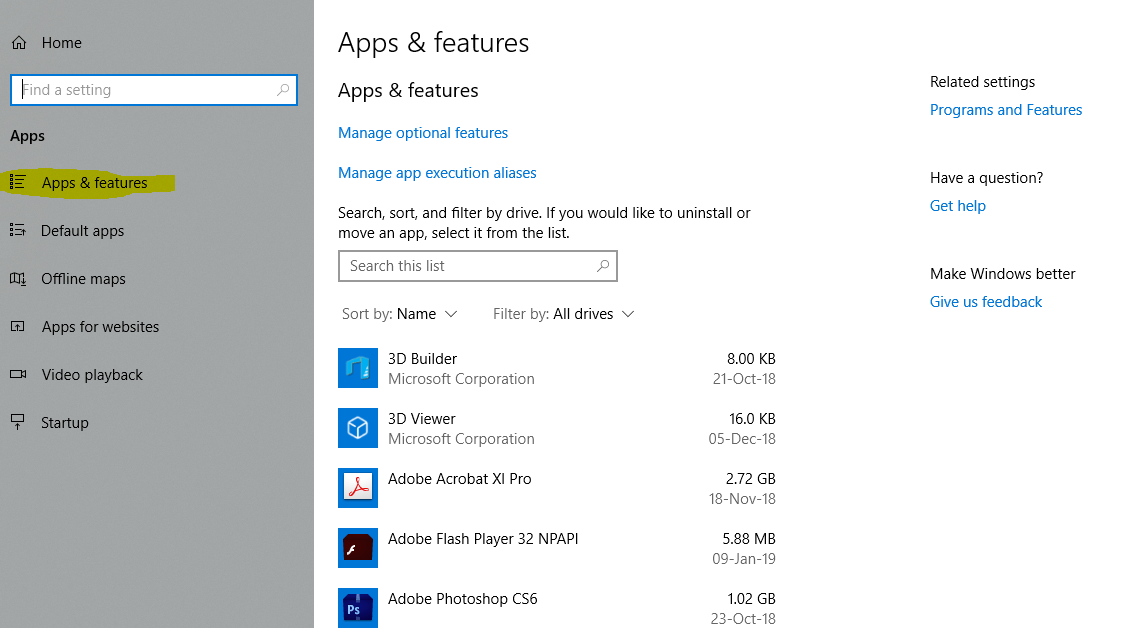
- Go to Settings.
2. Click on Apps within Settings.
3. Choose Apps & Features.
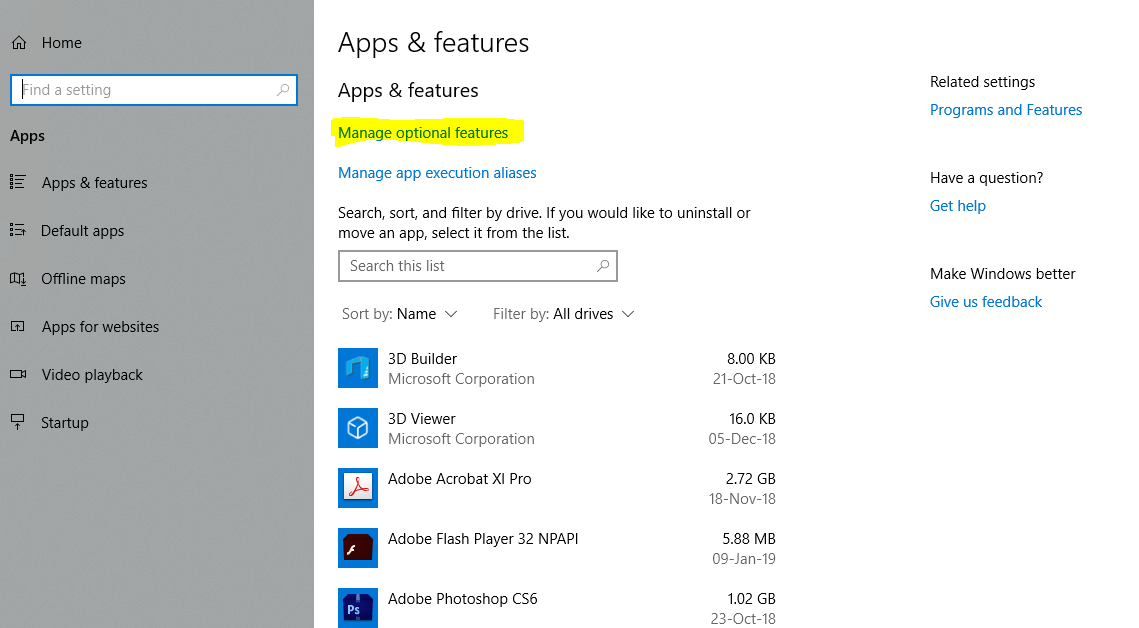
4. Click on Manage Optional Features.
Alternatively, despite Windows claiming the feature cannot be avoided, it appears that it may be possible to disable the reserved storage after all. This may be particularly beneficial if you have limited disk space, or simply resent not having control over your storage allocation.
Follow These Steps to Disable Reserved Storage:
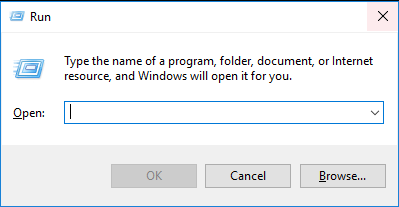
1. Press R + the Windows key.
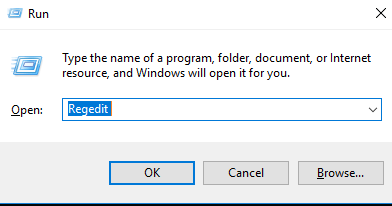
2. Type Regedit and press Enter.
3. Find HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager in Registry Editor.
4. Double click ShippedWithReserves and set value to 0.
5. Exit Registry Editor.
The reserve space can be reinstated by changing the value of ShippedWithReserves back to 1.
The update is due to begin around April 2019 but won’t appear overnight, so you have some time to decide whether this feature is for you. Given that over 700 million devices currently run Windows 10 operating systems, it’s likely to take a few months for the update to establish itself.