Cyber threats have evolved significantly over time, posing increasing risks to individuals, organizations, and governments in our interconnected world. Let’s explore the past, present, and future of cyber threats to better understand how to protect ourselves and our digital ecosystems.
Past: Emergence of Computer Viruses and Malware
- Computer viruses and malware have been a persistent threat in the past.
- These malicious programs exploit vulnerabilities in networks and devices.
- They can spread rapidly and cause significant damage to data and systems.
Present: Sophisticated Social Engineering Attacks and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
- In the present, cyber threats have become more sophisticated.
- Social engineering attacks manipulate individuals to gain unauthorized access to systems.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are targeted and persistent attacks that aim to steal sensitive information or disrupt operations.
- These threats pose significant challenges to cybersecurity defenses.
Future: New Vulnerabilities and Risks
- The future presents new vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
- The proliferation of mobile devices, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) creates a larger attack surface.
- Mobile devices can be targeted through malicious apps or vulnerabilities in operating systems.
- Cloud computing introduces new risks such as data breaches or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- The IoT expands the number of interconnected devices, making it harder to secure the entire network.
- Additionally, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) brings both transformative advancements and potential risks in cyber attacks.
Protecting Ourselves and Our Digital Ecosystems
- To better protect ourselves and our digital ecosystems, we need to stay informed about the latest cyber threats and security best practices.
- Regularly updating software and operating systems can help prevent vulnerabilities from being exploited.
- Implementing strong passwords and multi-factor authentication can add an extra layer of security.
- Educating ourselves and our organizations about social engineering techniques can help prevent falling victim to these attacks.
- Investing in robust cybersecurity solutions and regularly conducting vulnerability assessments can help identify and mitigate risks.
- Collaboration between individuals, organizations, and governments is crucial in sharing threat intelligence and developing effective cybersecurity strategies.
By understanding the evolution of cyber threats and taking proactive measures, we can enhance our cybersecurity defenses and minimize the impact of future attacks.
Early Computer Viruses
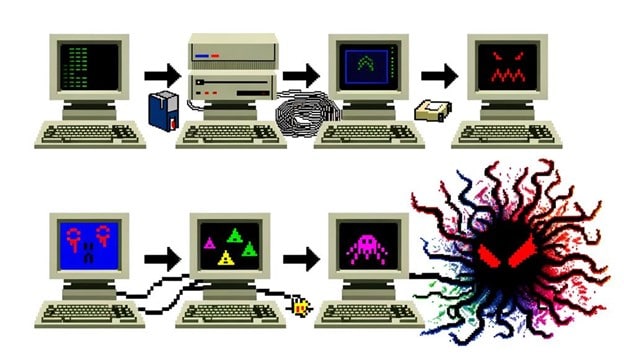
The emergence of early computer viruses during the dawn of the computer age marked a pivotal milestone in the evolution of cyber threats. These malicious programs, designed to replicate and spread, wreaked havoc on computer systems worldwide, causing significant damage and disrupting the emerging digital landscape. The history of cyberattacks can be traced back to these early viruses, serving as a wake-up call for the need to prioritize cybersecurity.
The first computer virus, the Creeper, was created in the early 1970s. It infected mainframe computers running the TENEX operating system and displayed a message that read, ‘I’m the creeper, catch me if you can!’ This event highlighted the vulnerability of computer systems to unauthorized access and manipulation, paving the way for the development of antivirus software.
Since then, cyber threats have evolved significantly, becoming more sophisticated and diverse. Today, we face not only viruses but also ransomware, phishing attacks, and advanced persistent threats, among others. Technology continues to advance, leading to more complex tactics employed by cybercriminals and posing future cybersecurity challenges.
To combat these evolving threats, organizations must stay vigilant and continuously update their defense mechanisms. This includes implementing robust cybersecurity measures, conducting regular risk assessments, and educating employees about potential threats. Collaboration between industry stakeholders and government entities is vital to address the ever-growing complexity of cyber threats and ensure a secure digital future.
Rise of Malware
The rise of malware has become a significant concern in the field of cybersecurity. To fully comprehend its impact on the digital landscape, it is crucial to explore the various types of malware, including viruses and ransomware. Additionally, understanding the consequences of malware attacks, such as data breaches and financial losses, is essential. Organizations must implement robust cybersecurity measures to defend against these threats.
Here, we delve into the world of malware, its types, and the steps organizations can take to protect themselves.
Malware, a shortened form of ‘malicious software,’ refers to any software specifically designed to harm or exploit computer systems. It encompasses a wide range of malicious programs that can infiltrate devices, networks, and servers. Let’s dive into the different types of malware:
- Viruses: These are the most well-known and traditional form of malware. Viruses attach themselves to files and programs, spreading from one device to another. When activated, they can corrupt or destroy data, leading to system malfunctions.
- Worms: Worms are self-replicating malware that spread across networks without the need for human intervention. They exploit vulnerabilities in operating systems and email systems to infect multiple devices quickly.
- Trojans: Named after the Greek mythological Trojan horse, Trojans masquerade as legitimate programs or files to deceive users into downloading them. Once installed, they can grant unauthorized access to hackers, allowing them to steal sensitive information or gain control over the system.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files on a victim’s device, rendering them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. It has become increasingly prevalent in recent years, targeting individuals, businesses, and even government organizations.
- Spyware: As the name suggests, spyware is designed to spy on users and gather sensitive information without their knowledge. It can track keystrokes, capture login credentials, and monitor online activities, posing a significant threat to privacy.
- Adware: Adware is a type of malware that displays unwanted advertisements on a user’s device. While not as harmful as other types of malware, it can be intrusive and negatively impact the user experience.
The consequences of malware attacks can be severe, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage. Data breaches resulting from malware can expose sensitive information, leading to identity theft and fraud. Organizations may also face legal consequences and regulatory fines if they fail to protect customer data adequately.
To defend against malware threats, organizations should implement robust cybersecurity measures. These can include:
- Installing and regularly updating antivirus software to detect and remove malware.
- Regularly backing up important data to ensure its availability in case of a malware attack.
- Keeping operating systems, software, and applications up to date with the latest security patches to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Implementing strong and unique passwords for all accounts and enabling two-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Educating employees about the risks of malware and the importance of practicing safe online behavior, such as avoiding suspicious email attachments and links.
- Conducting regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in the organization’s systems.
Malware Types Explained
Malware is a type of malicious software that poses a significant threat to computer systems. Understanding the different types of malware is essential for effective protection against these evolving cyber threats.
Below are four common types of malware:
- Viruses: Viruses are self-replicating programs that attach themselves to clean files and spread across devices. They cause damage to systems and can also steal sensitive information.
- Worms: Unlike viruses, worms are standalone programs that rapidly spread through networks. They take advantage of vulnerabilities and create network congestion, affecting the overall performance and stability of the network.
- Trojans: Named after the legendary Trojan horse, Trojans disguise themselves as legitimate software. However, they contain malicious code that allows unauthorized access to data. Once installed, Trojans can transfer sensitive information to hackers or even provide remote control access to the attacker.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is a particularly dangerous type of malware. It encrypts files on a victim’s computer, making them inaccessible. The attacker then demands a ransom payment in exchange for providing the decryption key. Ransomware attacks can have devastating consequences, especially for individuals or organizations that rely heavily on their data.
Impact on Cybersecurity
The rise of malware has had a significant impact on cybersecurity. Malware, which refers to malicious software that infiltrates and damages computer systems, poses serious threats to individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. This increase in malware has resulted in a surge of cyberattacks, data breaches, and financial losses.
To combat these threats, cybersecurity measures must continuously adapt to keep up with the ever-evolving tactics employed by cybercriminals.
Investing in robust antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems is crucial for organizations to detect and prevent malware infections. These tools provide essential protection against various types of malware, including viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware. By implementing such security measures, organizations can minimize the risk of malware infiltrating their systems and causing damage.
However, technological solutions alone are not enough. User education and awareness programs are vital in combating malware. Human error remains a significant factor in successful cyberattacks, as individuals can unknowingly click on malicious links or download infected files. By educating users about the risks and best practices for online security, organizations can empower their employees to make informed decisions and minimize the likelihood of malware infections.
Failure to address the impact of malware on cybersecurity can have severe consequences. Personal information can be compromised, leading to identity theft and financial ruin. Businesses may suffer financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences due to data breaches. Governments may face significant disruptions in critical infrastructure and national security.
Defense Against Malware
Organizations can adopt the following strategies to defend against the rise of malware:
- Implement Advanced Endpoint Protection: Deploy robust endpoint protection solutions that utilize machine learning algorithms and behavior-based analysis. These solutions can effectively detect and prevent malware infections, safeguarding the organization’s endpoints.
- Regularly Patch and Update Software: Ensure that all software and systems are kept up to date with the latest patches and security updates. By doing so, organizations can minimize vulnerabilities that malware can exploit, enhancing their overall security posture.
- Educate and Raise Employee Awareness: Provide comprehensive training to employees on safe browsing practices, recognizing phishing attempts, and maintaining good password hygiene. By educating employees about potential threats and best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of malware infections caused by human error.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Divide the network into segments to limit the spread of malware. By isolating critical systems and restricting lateral movement within the network, organizations can contain and mitigate the impact of malware infections.
Exploiting Network Vulnerabilities
Network vulnerability exploitation is a crucial aspect of cyber threats. Attackers target weaknesses in networks to gain unauthorized access, extract sensitive data, or disrupt operations. Understanding and implementing effective measures to minimize network vulnerabilities are essential for protection against evolving cyber threats.
Network vulnerability exploitation techniques involve identifying and taking advantage of weaknesses in network infrastructure, protocols, or configurations. These vulnerabilities can be exploited through various means, such as:
- Exploiting software vulnerabilities: Attackers search for and exploit weaknesses in software applications, operating systems, or firmware that are used in network devices. This can include leveraging known vulnerabilities or discovering new ones through techniques like reverse engineering.
- Social engineering: Attackers use psychological manipulation techniques to deceive network users into providing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise network security. This can include techniques like phishing, pretexting, or baiting.
- Brute force attacks: Attackers attempt to gain unauthorized access to network systems by systematically trying all possible combinations of usernames and passwords until they find the correct ones. This method is time-consuming but can be effective if weak or easily guessable passwords are used.
- Denial of service (DoS) attacks: Attackers overwhelm network resources, such as servers or routers, with an excessive amount of traffic, rendering them unavailable to legitimate users. This can disrupt network operations and cause significant downtime.
- Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks: Attackers intercept and alter network communications between two parties without their knowledge. This allows them to eavesdrop on sensitive information or modify data in transit.
To minimize network vulnerabilities and protect against exploitation, organizations should:
- Regularly update software and firmware: Keeping network devices, applications, and operating systems up to date with the latest security patches and updates helps protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Implement strong access controls: Enforcing strict password policies, implementing two-factor authentication, and limiting user privileges can help prevent unauthorized access to network resources.
- Conduct regular vulnerability assessments: Regularly scanning networks for vulnerabilities and conducting penetration tests can identify weaknesses before attackers exploit them.
- Train employees on cybersecurity best practices: Educating employees about the risks of social engineering attacks and providing training on how to recognize and respond to phishing emails or suspicious activities helps strengthen the human firewall.
- Implement network segmentation: Dividing networks into smaller, isolated segments can limit the potential impact of a successful attack and prevent lateral movement by attackers.
Network Weaknesses Exploited
Instances in the history of cyber threats have shown the exploitation of network weaknesses, underscoring the critical need to address vulnerabilities within digital infrastructure. Organizations can strengthen their defenses and mitigate risks by understanding the specific network weaknesses that cybercriminals commonly exploit.
The following are some frequently targeted network weaknesses:
- Outdated or unpatched software: Vulnerabilities in software create an easy entry point for attackers. Neglecting regular software updates and patches exposes networks to known vulnerabilities.
- Weak passwords and authentication measures: Inadequate passwords and lax authentication practices make it easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access to networks and sensitive information.
- Misconfigured network devices: Incorrectly configured routers, firewalls, and other network devices can create openings for cybercriminals to exploit, enabling them to gain control over the network.
- Lack of network monitoring and detection capabilities: Insufficient monitoring and detection systems make it challenging to identify and respond promptly to malicious activities, granting attackers more time to compromise the network.
Addressing these network weaknesses is crucial for organizations to protect their digital infrastructure and safeguard sensitive data from cyber threats.
Key Takeaways:
- Regular software updates and patches are essential to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Strong passwords and robust authentication practices are vital to secure network access.
- Proper configuration of network devices is crucial to avoid exploitable openings.
- Effective network monitoring and detection systems are necessary for timely response to malicious activities.
Vulnerability Exploitation Techniques
Network vulnerability exploitation is a crucial aspect of cyber threat tactics. It involves taking advantage of weaknesses or flaws in a network’s security protocols, configurations, or software to gain unauthorized access and compromise digital infrastructure. Attackers employ various methods to exploit these vulnerabilities, including:
- Exploiting unpatched software
- Employing brute force attacks to guess weak passwords
- Utilizing social engineering techniques to deceive users into divulging sensitive information
Once attackers gain entry into a network, they can escalate their privileges, move laterally across systems, and exfiltrate valuable data or launch additional attacks. To protect digital assets from exploitation, organizations must continually assess and mitigate network vulnerabilities. This includes regularly patching and updating software, implementing strong password policies, and providing cybersecurity awareness training to employees.
Minimizing Network Vulnerabilities
1. Regular vulnerability assessments:
Conducting routine vulnerability assessments helps identify weaknesses in the network infrastructure. This allows organizations to prioritize and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. By regularly assessing the network, organizations can stay one step ahead of potential threats.
2. Patch management:
Keeping software and systems up to date with the latest patches is crucial in reducing the risk of exploitation. Regularly applying patches ensures that known vulnerabilities are mitigated. By promptly addressing vulnerabilities through patch management, organizations can significantly improve their network security.
3. Network segmentation:
Implementing network segmentation helps limit the impact of a potential breach by isolating sensitive data or critical systems. By dividing the network into smaller segments, organizations can restrict unauthorized access and prevent the spread of an attack throughout the entire network. Network segmentation is a powerful defense mechanism against unauthorized access.
4. Employee education and awareness:
Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices and raising awareness about potential threats can significantly reduce the risk of network vulnerabilities. By promoting a culture of cybersecurity, organizations can empower their employees to identify and report suspicious activities promptly. Regular training sessions and communication channels for reporting security incidents are essential for maintaining a vigilant workforce.
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks pose a significant cybersecurity threat, exploiting human psychology to manipulate individuals and gain access to sensitive information or perform malicious actions. These attacks have become increasingly sophisticated and challenging to detect over time. Attackers employ tactics such as phishing, pretexting, baiting, and tailgating to deceive unsuspecting victims.
Phishing remains a common social engineering technique, where attackers send fraudulent emails pretending to be legitimate organizations. These emails trick recipients into clicking on malicious links or downloading harmful attachments. Pretexting involves creating false scenarios to gain victims’ trust and extract sensitive information. Baiting entices individuals with promises of rewards to lure them into revealing confidential data or performing malicious actions. Tailgating occurs when an unauthorized person gains entry to a secure area by closely following an authorized individual.
To mitigate the risk of social engineering attacks, organizations must prioritize employee awareness and education. Training programs should familiarize employees with common social engineering tactics, teaching them to recognize and respond appropriately to suspicious requests. Implementing strong authentication protocols, multi-factor authentication, and regularly updating security policies are crucial steps in safeguarding against these attacks.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)

Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are sophisticated and persistent cyber attacks that specifically target individuals, organizations, or nations in order to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or disrupt critical systems. Here are four key aspects to understand about APTs:
- APTs have a long-term focus: Unlike opportunistic attacks, APTs are meticulously planned and executed campaigns that can span over months or even years. Attackers patiently gather intelligence, exploit vulnerabilities, and maintain persistent access to their targets’ networks.
- APTs use customized techniques: To bypass security defenses and avoid detection, APTs employ highly tailored methods. Attackers leverage advanced malware, zero-day exploits, and social engineering tactics to compromise their targets’ systems and establish a foothold within their networks.
- APTs often involve nation-state actors: APTs are frequently associated with state-sponsored cyber espionage. Nation-states invest significant resources into developing APT capabilities for gathering intelligence, conducting cyber warfare, or achieving strategic objectives.
- APTs target high-value entities: APTs primarily focus on entities that possess valuable information, such as governments, defense contractors, financial institutions, and companies involved in cutting-edge research and development. The objective of these attacks is to steal classified information, intellectual property, or disrupt critical infrastructure.
As APTs continue to evolve and pose significant threats, it is crucial to invest in robust cybersecurity measures. This includes implementing threat intelligence, conducting network monitoring, and providing comprehensive employee education to detect and mitigate these persistent attacks.
Mobile Device Threats
Mobile devices have become an essential part of our everyday lives, both for personal and professional use. However, with their increasing capabilities, they have also become attractive targets for cybercriminals. Mobile device threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, and data breaches, pose significant risks to the security of our smartphones and tablets.
1. Malware: A Hidden Danger
- Malware is a common mobile device threat that can be distributed through malicious apps.
- These apps often masquerade as legitimate applications but contain hidden malicious code.
- Once installed, malware can compromise the security of your device, accessing sensitive information and even taking control remotely.
2. Phishing Attacks: Trickery at Your Fingertips
- Phishing attacks target users through fraudulent messages or websites, tricking them into revealing personal or financial information.
- Mobile devices are particularly vulnerable to these attacks due to their smaller screen size and the likelihood of users clicking on suspicious links.
3. Data Breaches: Protecting Your Sensitive Information
- With the increasing amount of sensitive data stored on smartphones and tablets, data breaches are a significant concern.
- Cybercriminals are constantly searching for vulnerabilities to exploit, which can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage.
To protect your mobile device from these threats, follow these precautions:
- Keep your device’s operating system and apps up to date: Regular updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities.
- Download apps only from trusted sources: Avoid third-party app stores and stick to official app stores like Google Play Store or Apple App Store.
- Be cautious of suspicious messages or links: Think twice before clicking on links in messages or emails, especially if they ask for personal information.
- Use strong and unique passwords: Choose passwords that are difficult to guess and avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
Cloud Security Challenges
Cloud security challenges encompass a complex landscape for organizations aiming to safeguard their data and systems in the digital era. As businesses increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, addressing the unique security challenges becomes paramount.
Here are four key challenges organizations face in maintaining cloud security:
- Data breaches: The risk of data breaches becomes more significant as the volume of sensitive data stored in the cloud increases. To protect their data from unauthorized access, organizations must implement robust security measures.
- Insider threats: Cloud environments rely on shared responsibilities between the cloud service provider and the organization, creating vulnerabilities that malicious insiders can exploit. To mitigate this risk, organizations need to implement strict access controls and monitoring mechanisms.
- Compliance and regulatory requirements: Operating in the cloud requires adherence to specific compliance and regulatory requirements based on different industries. Ensuring compliance can be challenging due to the dynamic and constantly evolving nature of cloud environments.
- Lack of visibility and control: Cloud environments often lack the same level of visibility and control found in on-premises systems. To gain insight into their cloud infrastructure and effectively respond to security incidents, organizations need to invest in advanced monitoring and threat detection tools.
Addressing these challenges necessitates a comprehensive approach that combines technology, processes, and employee awareness. It is crucial for organizations to prioritize cloud security and stay updated with the latest threats and best practices to effectively protect their data and systems.
Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities
Internet of Things (IoT) vulnerabilities are a major concern in today’s digital landscape. The interconnected nature of IoT devices, such as smart home appliances, wearable fitness trackers, and industrial sensors, has greatly expanded the potential attack surface for cybercriminals. These vulnerabilities arise from weak passwords, lack of encryption, and outdated firmware.
One of the main issues is the lack of standardization and security protocols across IoT devices. Many manufacturers prioritize functionality and cost-effectiveness over security, resulting in easily exploitable devices. Additionally, the large number of connected devices increases the likelihood of successful attacks. Once compromised, these devices can serve as entry points into larger networks or be used as botnets for launching large-scale attacks.
Another significant vulnerability is the data transmitted and stored by IoT devices. Personal and sensitive information, such as health records, home security footage, and location data, can be intercepted or accessed by cybercriminals without proper security measures. This not only compromises individual privacy but also poses a threat to national security.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial for manufacturers and users to prioritize security in the design and deployment of IoT devices. This includes implementing strong authentication mechanisms, regular security updates, and encryption protocols. Furthermore, users should be educated about the risks associated with IoT devices and encouraged to follow best practices, such as changing default passwords and keeping firmware up to date.
Only through a collective effort can we ensure the security and privacy of IoT devices in an increasingly connected world.
AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
AI-Powered cyber attacks are a rising threat in the digital landscape, utilizing advanced artificial intelligence technology to exploit vulnerabilities and elude traditional security measures. These attacks have the ability to learn and adapt in real-time, presenting significant challenges to both organizations and individuals.
Here are four important aspects to consider regarding AI-Powered cyber attacks:
- Automated reconnaissance: AI algorithms can efficiently scan vast amounts of data to identify potential targets and vulnerabilities. This automated reconnaissance process allows attackers to gather information quickly and select their targets more effectively.
- Sophisticated phishing campaigns: AI can create highly convincing phishing emails that are customized for specific individuals or organizations. These attacks can bypass traditional email filters and deceive even tech-savvy users into divulging sensitive information or installing malware.
- Adversarial machine learning: Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in machine learning models using AI. By injecting malicious data or manipulating the learning process, they can deceive AI systems, leading to incorrect decisions or actions.
- Evasive malware: AI-powered malware can actively avoid detection by adapting its behavior based on observed security measures. It can modify its code, alter its attack patterns, or conceal itself within legitimate network traffic, making it challenging for conventional security solutions to detect and mitigate.
As AI technology continues to advance, it is crucial for organizations to develop robust defense strategies that incorporate AI technologies to detect and counter these evolving threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does the Evolution of Cyber Threats Impact Individuals and Businesses on a Daily Basis?
The daily impact of the evolving cyber threats is significant for individuals and businesses. These threats expose them to various risks, including data breaches, financial losses, reputation damage, and operational disruptions. To mitigate these risks, robust cybersecurity measures are crucial. Let’s explore how the evolution of cyber threats affects individuals and businesses on a daily basis:
- Increased Vulnerability: With the advancement of technology, cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks. This puts individuals and businesses at a higher risk of being targeted by cyberattacks.
- Data Breaches: Cyber threats can lead to data breaches, where sensitive information such as personal data, financial records, and intellectual property is compromised. This can have severe consequences for individuals and businesses, including financial loss, identity theft, and legal ramifications.
- Financial Loss: Cyberattacks can result in significant financial losses for businesses. These losses can be due to theft of funds, ransom payments, legal fees, and the cost of recovering from the attack. For individuals, financial losses can occur through fraudulent transactions and unauthorized access to bank accounts.
- Reputation Damage: Cyberattacks can tarnish the reputation of individuals and businesses. Data breaches and other cyber incidents can erode trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders. This can lead to a loss of business opportunities and damage to long-term relationships.
- Disruption of Operations: Cyber threats can disrupt the smooth functioning of businesses. Ransomware attacks, for example, can encrypt critical data and bring operations to a standstill until a ransom is paid. This can result in downtime, loss of productivity, and potential financial repercussions.
- Regulatory Compliance: The evolving cyber threats also necessitate compliance with various regulations and standards. Businesses need to adhere to data protection laws, industry regulations, and cybersecurity frameworks to ensure the security of their systems and the privacy of customer data.
- Increased Security Costs: As cyber threats continue to evolve, businesses must invest in advanced security measures to protect their systems and networks. This includes implementing robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption technologies, and employee training programs. These security measures can be costly but are essential to safeguard against potential cyberattacks.
- Need for Vigilance: Individuals and businesses must be vigilant in identifying and addressing cyber threats on a daily basis. This includes regularly updating software, using strong passwords, practicing safe browsing habits, and being cautious of phishing attempts.
To effectively mitigate the impact of evolving cyber threats, individuals and businesses must prioritize cybersecurity measures and stay abreast of the latest trends and best practices in the field. By doing so, they can better protect themselves from potential risks and ensure the security of their digital assets.
What Are Some Key Strategies That Individuals and Businesses Can Employ to Protect Themselves Against Emerging Cyber Threats?
One effective strategy for protecting against emerging cyber threats is to regularly update software. This ensures that security patches and fixes are in place to address any vulnerabilities that may be exploited by hackers. Additionally, using strong and unique passwords is crucial. Passwords should be a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, and should not be easily guessable. Employing multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a fingerprint.
Education is another key strategy. By educating employees on cybersecurity best practices, businesses can reduce the risk of human error leading to a breach. This can include training on how to identify and avoid phishing emails, how to create and manage secure passwords, and how to recognize and report suspicious activity.
Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is also important. This may include using firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems to protect against unauthorized access and malware. Regularly backing up data is essential to ensure that it can be recovered in the event of a cyber attack or data loss. Encrypting sensitive data can provide an additional layer of protection, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to access or read the information.
How Are Cybercriminals Adapting Their Tactics and Techniques to Take Advantage of Advancements in Technology?
Cybercriminals continuously adapt their tactics and techniques to exploit advancements in technology. They target vulnerabilities in software, employ sophisticated phishing and social engineering methods, and leverage the anonymity of the dark web to carry out their malicious activities.
To take advantage of technological advancements, cybercriminals:
- Exploit software vulnerabilities: They identify weaknesses in software and exploit them to gain unauthorized access or control over systems and networks. This can include exploiting outdated software versions or zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Utilize sophisticated phishing techniques: Cybercriminals employ deceptive tactics to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information, such as passwords or financial details. They may use convincing emails, fake websites, or even phone calls to manipulate victims.
- Engage in social engineering: Cybercriminals manipulate human psychology to deceive individuals or gain unauthorized access to systems. They may impersonate trusted entities, use social media platforms for reconnaissance, or exploit personal relationships to extract sensitive information.
- Leverage the anonymity of the dark web: The dark web is a hidden part of the internet that allows cybercriminals to anonymously buy and sell illegal goods, services, and information. They utilize this anonymity to carry out illicit activities, such as selling stolen data, distributing malware, or coordinating cyber attacks.
Are There Any Specific Industries or Sectors That Are More Vulnerable to Cyber Threats? if So, Why?
Certain industries or sectors are more vulnerable to cyber threats due to several factors. These include the value of their data, the level of digitalization, and the potential impact on critical infrastructure. Here are some examples of industries that are particularly susceptible to cyber threats:
- Financial Services: The financial services industry handles a vast amount of valuable data, including personal and financial information. This makes it an attractive target for cybercriminals seeking to steal sensitive data or conduct financial fraud.
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry holds a wealth of personal and medical data, making it a prime target for hackers. Cyber attacks on healthcare organizations can compromise patient privacy, disrupt healthcare services, and even threaten patient safety.
- Energy and Utilities: The energy and utilities sector operates critical infrastructure such as power grids and water treatment plants. A cyber attack on these systems can have severe consequences, including power outages, infrastructure damage, and even public safety risks.
- Government and Defense: Government agencies and defense organizations store sensitive information related to national security and defense strategies. Cyber attacks targeting these entities can lead to espionage, disruption of critical services, or even compromise classified information.
- Manufacturing: The manufacturing sector increasingly relies on interconnected systems and automation, known as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). This reliance on technology exposes manufacturers to cyber threats that can disrupt production processes, compromise intellectual property, or cause supply chain disruptions.
- Retail and E-commerce: Retailers and e-commerce platforms handle large volumes of customer data, including payment information. Cyber attacks targeting these sectors can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and the compromise of customer data.
- Education: The education sector is becoming more digitally driven, with the use of online learning platforms and student information systems. Cyber attacks on educational institutions can lead to data breaches, disruption of educational services, and identity theft.
These industries face a higher risk of cyber threats due to the value and sensitivity of the data they handle, as well as the potential impact on critical infrastructure and public safety. It is crucial for organizations in these sectors to prioritize cybersecurity measures and develop robust defense strategies to mitigate these risks.
What Role Does Government Regulation and International Cooperation Play in Mitigating Cyber Threats and Ensuring Cybersecurity?
Government regulation and international cooperation are essential in mitigating cyber threats and ensuring cybersecurity. They serve as the foundation of defense, providing guidelines, standards, and collaboration platforms to address the complex and ever-evolving challenges in the digital landscape.
1. Government regulation:
- Governments establish regulatory frameworks that outline the legal requirements for cybersecurity. These regulations set standards for data protection, privacy, and the secure handling of sensitive information.
- Regulatory bodies enforce compliance with these standards, conducting audits and investigations to ensure that organizations adhere to cybersecurity best practices.
- Regulations also outline the consequences for non-compliance, such as fines or legal action, incentivizing organizations to prioritize cybersecurity measures.
2. International cooperation:
- Cyber threats are not limited by national borders, and international cooperation is crucial to effectively combat them. Countries collaborate to share information, intelligence, and best practices to enhance their collective cybersecurity capabilities.
- International agreements and alliances, such as mutual defense pacts and information-sharing frameworks, facilitate cooperation and coordination among nations in responding to cyberattacks.
- Joint exercises and training programs enable countries to enhance their cybersecurity readiness and build capacity to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats.
3. Information sharing and collaboration:
- Governments and international organizations create platforms and networks for sharing information and collaborating on cybersecurity issues. These platforms enable the timely exchange of threat intelligence, vulnerabilities, and mitigation strategies.
- Public-private partnerships facilitate collaboration between government agencies and private sector entities, leveraging their respective expertise and resources to enhance cybersecurity measures.
- Collaboration also extends to academia, where research institutions contribute to the development of innovative cybersecurity solutions and the training of cybersecurity professionals.
Harmonization of cybersecurity standards:
- Governments and international bodies work together to establish common cybersecurity standards and frameworks. This harmonization ensures that organizations operating across borders adhere to consistent security practices.
- Standardization promotes interoperability and compatibility of cybersecurity technologies and solutions, enabling effective defense against cyber threats at a global scale.
- International collaboration also helps address emerging challenges, such as the regulation of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, ensuring that cybersecurity considerations are integrated into their development and deployment.
Conclusion
The evolution of cyber threats has been a perilous journey, filled with challenges and risks at every step. From the inception of computer viruses to the tactics employed by advanced persistent threats (APTs), the cyber landscape has grown increasingly complex and menacing. It is essential for individuals, organizations, and nations to remain vigilant and proactive in their approach to cybersecurity as technology continues to advance. By understanding the past and present trends, we can better prepare for the future and protect against the constant specter of cyber attacks.
In the early days of cyber threats, computer viruses emerged as a significant concern. These malicious software programs replicate themselves and spread from one computer to another, often causing damage or stealing sensitive information. As technology evolved, so did the tactics of cybercriminals. Hackers began to utilize more sophisticated methods, such as phishing and social engineering, to deceive individuals and gain unauthorized access to their systems.
The rise of APTs marked a turning point in the world of cyber threats. APTs are highly organized and well-funded groups that employ advanced techniques to infiltrate networks and maintain long-term access. These threats often target government agencies, corporations, and critical infrastructure, with the goal of espionage, sabotage, or financial gain. APTs employ tactics like zero-day exploits, custom malware, and targeted phishing attacks to breach their targets undetected.
As we look to the future, the landscape of cyber threats is expected to become even more complex. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and quantum computing present both opportunities and challenges in the realm of cybersecurity. With the increasing interconnectedness of devices and systems, the attack surface for cybercriminals expands, making it more crucial than ever to prioritize security measures.
To combat the evolving threats, individuals and organizations must adopt a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity. This includes implementing robust firewalls, regularly updating software and systems, employing strong encryption, and educating users about best practices for safe online behavior. Additionally, cooperation between governments, international organizations, and cybersecurity firms is vital to sharing threat intelligence and collaborating on defense strategies.
In conclusion, the evolution of cyber threats has necessitated constant adaptation and innovation in the field of cybersecurity. By staying informed about past and present trends, we can better equip ourselves to face the challenges of the future. It is imperative that we remain proactive and diligent in safeguarding our digital assets and infrastructure from the ever-present danger of cyber attacks.
